Medicine
Types of Degrees Medicine Majors Are Getting
The following table lists how many medicine graduations there were for each degree level during the last year for which data was available.
| Education Level | Number of Grads |
|---|---|
| Doctor’s Degree | 29,168 |
| Graduate Certificate | 38 |
What Medicine Majors Need to Know
In an O*NET survey, medicine majors were asked to rate what knowledge areas, skills, and abilities were important in their occupations. These answers were weighted on a scale of 1 to 5 with 5 being the most important.
Knowledge Areas for Medicine Majors
According to O*NET survey takers, a major in medicine should prepare you for careers in which you will need to be knowledgeable in the following areas:
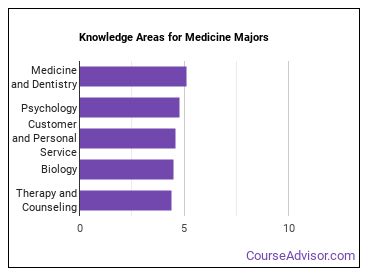
- Medicine and Dentistry - Knowledge of the information and techniques needed to diagnose and treat human injuries, diseases, and deformities. This includes symptoms, treatment alternatives, drug properties and interactions, and preventive health-care measures.
- Psychology - Knowledge of human behavior and performance; individual differences in ability, personality, and interests; learning and motivation; psychological research methods; and the assessment and treatment of behavioral and affective disorders.
- Customer and Personal Service - Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
- Biology - Knowledge of plant and animal organisms, their tissues, cells, functions, interdependencies, and interactions with each other and the environment.
- Therapy and Counseling - Knowledge of principles, methods, and procedures for diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of physical and mental dysfunctions, and for career counseling and guidance.
Skills for Medicine Majors
medicine majors are found most commonly in careers in which the following skills are important:
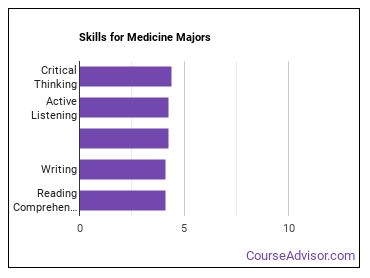
- Critical Thinking - Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
- Active Listening - Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
- Judgment and Decision Making - Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
- Reading Comprehension - Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
- Writing - Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Abilities for Medicine Majors
As you progress with your medicine degree, there are several abilities you should pick up that will help you in whatever related career you choose. These abilities include:
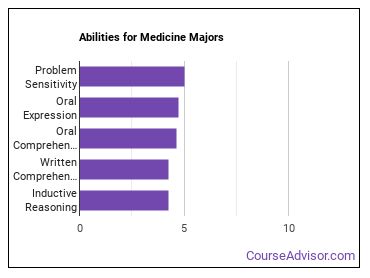
- Problem Sensitivity - The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
- Oral Expression - The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
- Oral Comprehension - The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
- Written Comprehension - The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
- Inductive Reasoning - The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
What Can You Do With a Medicine Major?
Below is a list of occupations associated with medicine:
| Job Title | Job Growth Rate | Median Salary |
|---|---|---|
| Family and General Practitioners | 14.3% | $201,100 |
| Physicians and Surgeons | 11.4% | $200,890 |
Amount of Education Required for Careers Related to Medicine
Some careers associated with medicine require an advanced degree while some may not even require a bachelor’s. Whatever the case may be, pursuing more education usually means that more career options will be available to you.
Find out what the typical degree level is for medicine careers below.
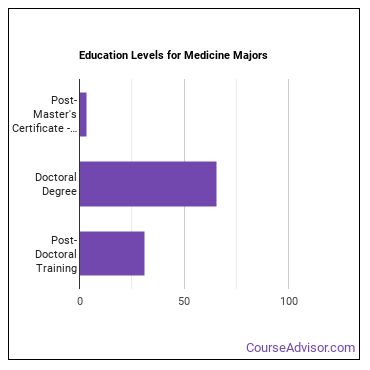
| Education Level | Percentage of Workers |
|---|---|
| Post-Master’s Certificate - awarded for completion of an organized program of study; designed for people who have completed a Master’s degree but do not meet the requirements of academic degrees at the doctoral level. | 3.5% |
| Doctoral Degree | 65.4% |
| Post-Doctoral Training | 31.1% |
Online Medicine Programs
The following table lists the number of programs by degree level, along with how many schools offered online courses in the field.
| Degree Level | Colleges Offering Programs | Colleges Offering Online Classes |
|---|---|---|
| Certificate (Less Than 1 Year) | 0 | 0 |
| Certificate (1-2 years) | 0 | 0 |
| Certificate (2-4 Years) | 0 | 0 |
| Associate’s Degree | 0 | 0 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 0 | 0 |
| Post-Baccalaureate | 0 | 0 |
| Master’s Degree | 0 | 0 |
| Post-Master’s | 4 | 0 |
| Doctor’s Degree (Research) | 1 | 0 |
| Doctor’s Degree (Professional Practice) | 198 | 0 |
| Doctor’s Degree (Other) | 0 | 0 |
Explore Major by State
Alabama
California
District of Columbia
Idaho
Kansas
Maryland
Mississippi
Nevada
New York
Oklahoma
South Carolina
Utah
West Virginia
Alaska
Colorado
Florida
Illinois
Kentucky
Massachusetts
Missouri
New Hampshire
North Carolina
Oregon
South Dakota
Vermont
Wisconsin
Majors Related to Medicine
You may also be interested in one of the following majors related to medicine.
References
*The racial-ethnic minorities count is calculated by taking the total number of students and subtracting white students, international students, and students whose race/ethnicity was unknown. This number is then divided by the total number of students at the school to obtain the racial-ethnic minorities percentage.
- College Factual
- College Scorecard
- National Center for Education Statistics
- O*NET Online
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- Usual Weekly Earnings of Wage and Salary Workers First Quarter 2020
More about our data sources and methodologies.
