What Do Materials Scientist Do?
Materials Scientist Job Description Research and study the structures and chemical properties of various natural and synthetic or composite materials, including metals, alloys, rubber, ceramics, semiconductors, polymers, and glass. Determine ways to strengthen or combine materials or develop new materials with new or specific properties for use in a variety of products and applications. Includes glass scientists, ceramic scientists, metallurgical scientists, and polymer scientists.
Life As a Materials Scientist: What Do They Do?
- Confer with customers to determine how to tailor materials to their needs.
- Perform experiments and computer modeling to study the nature, structure, and physical and chemical properties of metals and their alloys, and their responses to applied forces.
- Test metals to determine conformance to specifications of mechanical strength, strength-weight ratio, ductility, magnetic and electrical properties, and resistance to abrasion, corrosion, heat, and cold.
- Conduct research on the structures and properties of materials, such as metals, alloys, polymers, and ceramics, to obtain information that could be used to develop new products or enhance existing ones.
- Determine ways to strengthen or combine materials or develop new materials with new or specific properties for use in a variety of products and applications.
- Supervise and monitor production processes to ensure efficient use of equipment, timely changes to specifications, and project completion within time frame and budget.
Featured schools near , edit
What Every Materials Scientist Should Know
When polled, Materials Scientists say the following skills are most frequently used in their jobs:
Science: Using scientific rules and methods to solve problems.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Judgment and Decision Making: Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Related Job Titles
- Nanotechnologist
- Staff Research Scientist
- Technology Officer
- Metal Alloy Scientist
- Plastics Scientist
Is There Job Demand for Materials Scientists?
There were about 7,900 jobs for Materials Scientist in 2016 (in the United States). New jobs are being produced at a rate of 7.6% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 600 new jobs for Materials Scientist by 2026. Due to new job openings and attrition, there will be an average of 800 job openings in this field each year.
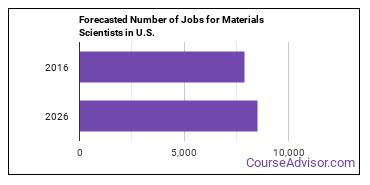
The states with the most job growth for Materials Scientist are Utah, Idaho, and Missouri. Watch out if you plan on working in Illinois, Washington, or Tennessee. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
What is the Average Salary of a Materials Scientist
The typical yearly salary for Materials Scientists is somewhere between $52,560 and $159,970.
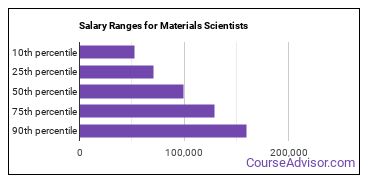
Materials Scientists who work in New Mexico, Connecticut, or Indiana, make the highest salaries.
How much do Materials Scientists make in different U.S. states?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $66,170 |
| Arizona | $91,870 |
| California | $102,860 |
| Colorado | $111,890 |
| Connecticut | $123,590 |
| Delaware | $88,630 |
| Florida | $104,710 |
| Georgia | $84,940 |
| Illinois | $94,920 |
| Indiana | $125,320 |
| Iowa | $87,010 |
| Louisiana | $110,820 |
| Maine | $66,990 |
| Maryland | $105,180 |
| Massachusetts | $97,240 |
| Michigan | $84,700 |
| Minnesota | $98,690 |
| Missouri | $91,530 |
| Nevada | $121,420 |
| New Hampshire | $105,330 |
| New Jersey | $104,530 |
| New Mexico | $136,130 |
| New York | $101,310 |
| North Carolina | $114,900 |
| Ohio | $100,360 |
| Oregon | $102,140 |
| Pennsylvania | $100,950 |
| South Carolina | $79,260 |
| Tennessee | $82,660 |
| Texas | $120,320 |
| Utah | $91,390 |
| Virginia | $101,950 |
What Tools do Materials Scientists Use?
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Materials Scientists may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Web browser software
- Email software
- The MathWorks MATLAB
- IBM SPSS Statistics
- R
- National Instruments LabVIEW
- Wolfram Research Mathematica
- Maplesoft Maple
- ANSYS Multiphysics
- Dassault Systemes Abaqus
- ANSYS LS-DYNA
How to Become a Materials Scientist
Education needed to be a Materials Scientist:
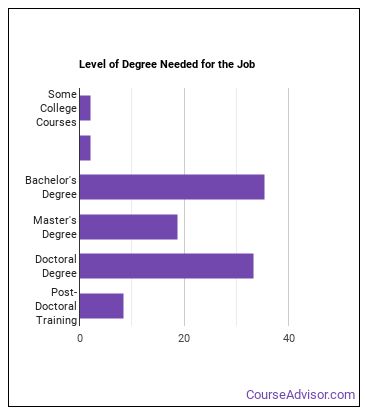
What work experience do I need to become a Materials Scientist?
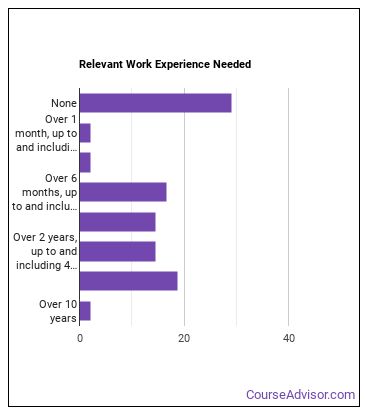
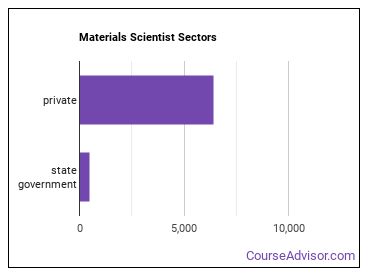
Who Employs Materials Scientists?
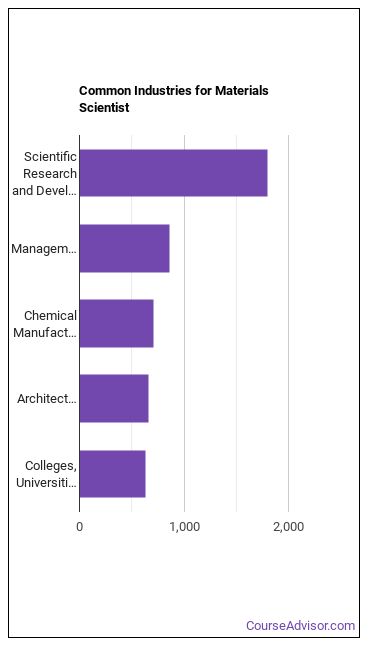
Materials Scientists work in the following industries:
Related Careers
Those thinking about becoming a Materials Scientist might also be interested in the following careers:
Are you already one of the many Materials Scientist in the United States? If you’re thinking about changing careers, these fields are worth exploring:
References:
Image Credit: Per Henning via Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
