Agricultural Production
Types of Degrees Agricultural Production Majors Are Getting
The following table lists how many agricultural production graduations there were for each degree level during the last year for which data was available.
| Education Level | Number of Grads |
|---|---|
| Associate Degree | 1,167 |
| Basic Certificate | 1,039 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 687 |
| Undergraduate Certificate | 436 |
| Master’s Degree | 144 |
| Doctor’s Degree | 26 |
| Graduate Certificate | 23 |
What Agricultural Production Majors Need to Know
O*NET surveyed people in occupations related to agricultural production and asked them what knowledge areas, skills, and abilities were important for their jobs. The responses were rated on a scale of 1 to 5 with 5 being most important.
Knowledge Areas for Agricultural Production Majors
Agricultural Production majors often go into careers in which the following knowledge areas are important:
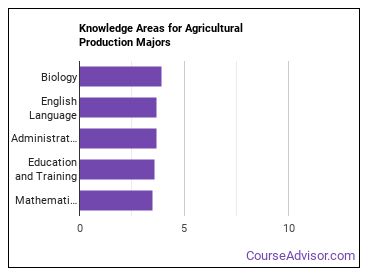
- Biology - Knowledge of plant and animal organisms, their tissues, cells, functions, interdependencies, and interactions with each other and the environment.
- English Language - Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
- Administration and Management - Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
- Education and Training - Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
- Mathematics - Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, and their applications.
Skills for Agricultural Production Majors
agricultural production majors are found most commonly in careers in which the following skills are important:
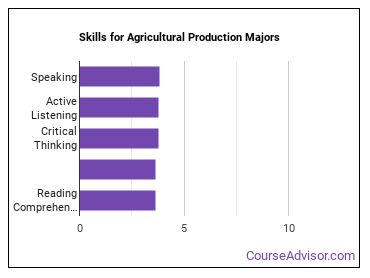
- Speaking - Talking to others to convey information effectively.
- Active Listening - Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
- Critical Thinking - Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
- Judgment and Decision Making - Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
- Reading Comprehension - Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Abilities for Agricultural Production Majors
A major in agricultural production will prepare for your careers in which the following abilities are important:
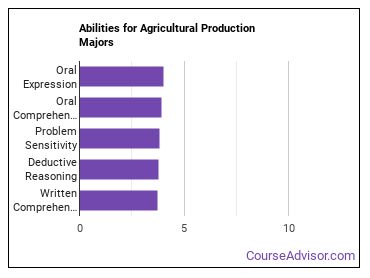
- Oral Expression - The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
- Oral Comprehension - The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
- Problem Sensitivity - The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
- Deductive Reasoning - The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
- Written Comprehension - The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
What Can You Do With a Agricultural Production Major?
Below is a list of occupations associated with agricultural production:
| Job Title | Job Growth Rate | Median Salary |
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Sciences Professors | 7.9% | $84,640 |
| Animal Breeders | 2.2% | $37,060 |
| Farm and Home Management Advisors | 7.7% | $49,840 |
| First-Line Supervisors of Agricultural Crop and Horticultural Workers | 2.1% | $46,960 |
| First-Line Supervisors of Animal Husbandry and Animal Care Workers | 2.1% | $46,960 |
| First-Line Supervisors of Aquacultural Workers | 2.1% | $46,960 |
| Food Scientists and Technologists | 5.9% | $65,300 |
| Forestry & Conservation Science Professors | 4.5% | $86,900 |
| Soil and Plant Scientists | 9.0% | $63,950 |
| Soil and Water Conservationists | 6.3% | $61,310 |
Who Is Getting a Bachelor’s Degree in Agricultural Production?
Racial-Ethnic Diversity
At the countrywide level, the racial-ethnic distribution of agricultural production majors is as follows:
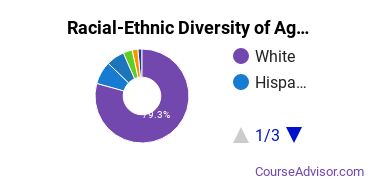
| Race/Ethnicity | Number of Grads |
|---|---|
| Asian | 14 |
| Black or African American | 25 |
| Hispanic or Latino | 60 |
| White | 535 |
| International Students | 7 |
| Other Races/Ethnicities | 46 |
Geographic Diversity
Americans aren’t the only ones with an interest in Agricultural Production. About 1.0% of those with this major are international students.
Amount of Education Required for Careers Related to Agricultural Production
Some degrees associated with agricultural production may require an advanced degree, while others may not even require a bachelor’s in the field. In general, the more advanced your degree the more career options will open up to you. However, there is significant time and money that needs to be invested into your education so weigh the pros and cons.
How much schooling do you really need to compete in today’s job market? People currently working in careers related to agricultural production have obtained the following education levels.
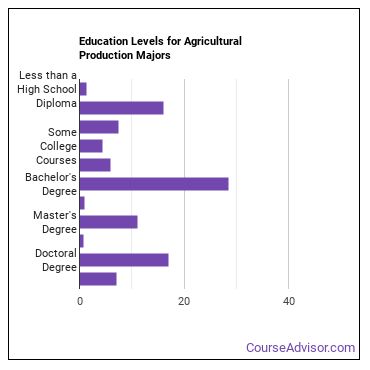
| Education Level | Percentage of Workers |
|---|---|
| Less than a High School Diploma | 1.4% |
| High School Diploma - or the equivalent (for example, GED) | 16.0% |
| Post-Secondary Certificate - awarded for training completed after high school (for example, in agriculture or natural resources, computer services, personal or culinary services, engineering technologies, healthcare, construction trades, mechanic and repair technologies, or precision production) | 7.4% |
| Some College Courses | 4.4% |
| Associate’s Degree (or other 2-year degree) | 5.9% |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 28.6% |
| Post-Baccalaureate Certificate - awarded for completion of an organized program of study; designed for people who have completed a Baccalaureate degree but do not meet the requirements of academic degrees carrying the title of Master. | 1.0% |
| Master’s Degree | 11.0% |
| Post-Master’s Certificate - awarded for completion of an organized program of study; designed for people who have completed a Master’s degree but do not meet the requirements of academic degrees at the doctoral level. | 0.7% |
| Doctoral Degree | 17.1% |
| Post-Doctoral Training | 7.0% |
Online Agricultural Production Programs
The following table lists the number of programs by degree level, along with how many schools offered online courses in the field.
| Degree Level | Colleges Offering Programs | Colleges Offering Online Classes |
|---|---|---|
| Certificate (Less Than 1 Year) | 0 | 0 |
| Certificate (1-2 years) | 106 | 1 |
| Certificate (2-4 Years) | 5 | 0 |
| Associate’s Degree | 209 | 4 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 15 | 3 |
| Post-Baccalaureate | 0 | 0 |
| Master’s Degree | 22 | 4 |
| Post-Master’s | 0 | 0 |
| Doctor’s Degree (Research) | 9 | 0 |
| Doctor’s Degree (Professional Practice) | 0 | 0 |
| Doctor’s Degree (Other) | 0 | 0 |
Explore Major by State
Alabama
California
District of Columbia
Idaho
Kansas
Maryland
Mississippi
Nevada
New York
Oklahoma
South Carolina
Utah
West Virginia
Alaska
Colorado
Florida
Illinois
Kentucky
Massachusetts
Missouri
New Hampshire
North Carolina
Oregon
South Dakota
Vermont
Wisconsin
Majors Related to Agricultural Production
You may also be interested in one of the following majors related to agricultural production.
| Major | Number of Grads |
|---|---|
| Animal Science | 8,396 |
| Veterinary/Animal Health Technologies/Technicians | 8,257 |
| Agricultural Economics & Business | 8,085 |
| Horticulture | 3,932 |
| Veterinary Medicine | 3,555 |
| Plant Sciences | 3,307 |
| General Agriculture | 3,256 |
| Food Science Technology | 2,181 |
| Agricultural Mechanization | 1,402 |
| Animal Services | 1,217 |
| Veterinary Biomedical and Clinical Sciences | 954 |
| Agricultural Public Services | 866 |
| Other Agriculture | 700 |
| Agriculture/Veterinary Preparatory Programs | 486 |
| Soil Sciences | 439 |
| International Agriculture | 215 |
| Food Processing | 198 |
| Veterinary Administrative Services | 113 |
References
*The racial-ethnic minorities count is calculated by taking the total number of students and subtracting white students, international students, and students whose race/ethnicity was unknown. This number is then divided by the total number of students at the school to obtain the racial-ethnic minorities percentage.
- College Factual
- College Scorecard
- National Center for Education Statistics
- O*NET Online
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- Usual Weekly Earnings of Wage and Salary Workers First Quarter 2020
- Image Credit: By {} under License
More about our data sources and methodologies.
