What You Need to Know About Food Scientist or Technologist
Career Description Use chemistry, microbiology, engineering, and other sciences to study the principles underlying the processing and deterioration of foods; analyze food content to determine levels of vitamins, fat, sugar, and protein; discover new food sources; research ways to make processed foods safe, palatable, and healthful; and apply food science knowledge to determine best ways to process, package, preserve, store, and distribute food.
Food Scientist or Technologist Responsibilities
- Study methods to improve aspects of foods, such as chemical composition, flavor, color, texture, nutritional value, and convenience.
- Stay up to date on new regulations and current events regarding food science by reviewing scientific literature.
- Develop food standards and production specifications, safety and sanitary regulations, and waste management and water supply specifications.
- Seek substitutes for harmful or undesirable additives, such as nitrites.
- Confer with process engineers, plant operators, flavor experts, and packaging and marketing specialists to resolve problems in product development.
- Develop new or improved ways of preserving, processing, packaging, storing, and delivering foods, using knowledge of chemistry, microbiology, and other sciences.
Featured schools near , edit
Food Scientist or Technologist Skills
When polled, Food Scientists and Technologists say the following skills are most frequently used in their jobs:
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Writing: Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Active Learning: Understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Related Job Titles
- Research Chef
- Food Chemist
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point Coordinator (HACCP Coordinator)
- Research Food Technologist
- Quality Control Scientist (QC Scientist)
Is There Job Demand for Food Scientists and Technologists?
There were about 17,000 jobs for Food Scientist or Technologist in 2016 (in the United States). New jobs are being produced at a rate of 5.9% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 1,000 new jobs for Food Scientist or Technologist by 2026. There will be an estimated 1,800 positions for Food Scientist or Technologist per year.
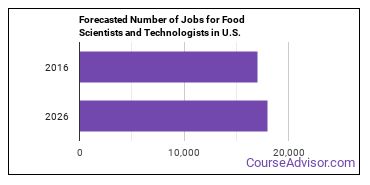
The states with the most job growth for Food Scientist or Technologist are Utah, Colorado, and Arkansas. Watch out if you plan on working in Washington, Vermont, or South Carolina. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Salary for a Food Scientist or Technologist
The average yearly salary of a Food Scientist or Technologist ranges between $39,510 and $118,630.
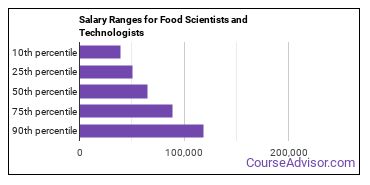
Food Scientists and Technologists who work in District of Columbia, Illinois, or Massachusetts, make the highest salaries.
Below is a list of the median annual salaries for Food Scientists and Technologists in different U.S. states.
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $54,340 |
| Arizona | $65,100 |
| Arkansas | $84,580 |
| California | $72,580 |
| Colorado | $68,520 |
| Connecticut | $81,290 |
| District of Columbia | $97,570 |
| Florida | $76,740 |
| Georgia | $65,500 |
| Idaho | $67,600 |
| Illinois | $89,700 |
| Indiana | $72,760 |
| Iowa | $67,360 |
| Kansas | $76,380 |
| Kentucky | $58,260 |
| Maine | $52,000 |
| Maryland | $87,530 |
| Massachusetts | $87,700 |
| Michigan | $59,610 |
| Minnesota | $80,320 |
| Missouri | $65,190 |
| Nebraska | $72,100 |
| New Jersey | $78,560 |
| New York | $61,630 |
| North Carolina | $58,430 |
| Ohio | $78,950 |
| Oklahoma | $54,720 |
| Oregon | $65,750 |
| Pennsylvania | $76,670 |
| Rhode Island | $73,400 |
| South Dakota | $56,150 |
| Tennessee | $60,330 |
| Texas | $67,500 |
| Utah | $59,890 |
| Vermont | $86,360 |
| Virginia | $67,950 |
| Washington | $62,830 |
| Wisconsin | $63,140 |
What Tools do Food Scientists and Technologists Use?
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Food Scientists and Technologists may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- SAP
- Insightful S-PLUS
- STATISTICA
- Image analysis software
How to Become a Food Scientist or Technologist
What education or degrees do I need to become a Food Scientist or Technologist?
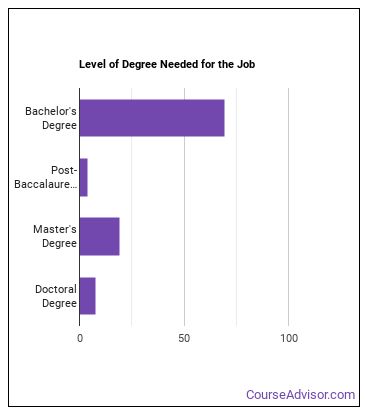
How Long Does it Take to Become a Food Scientist or Technologist?
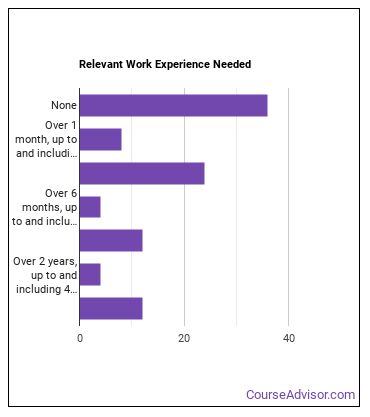
Food Scientists and Technologists Sector
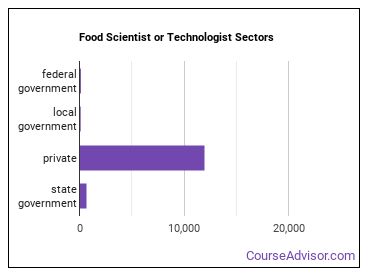
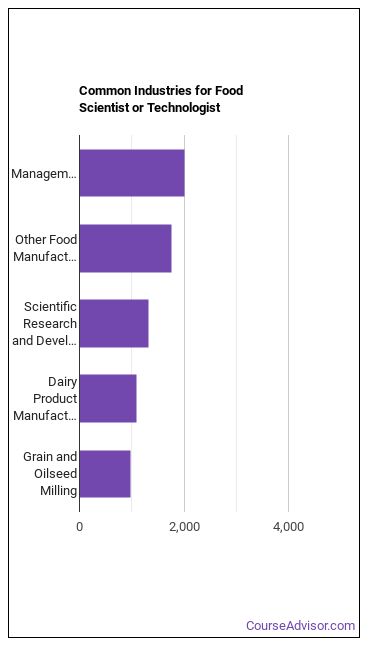
Below are examples of industries where Food Scientists and Technologists work:
Similar Careers
Those interested in being a Food Scientist or Technologist may also be interested in:
Those who work as a Food Scientist or Technologist sometimes switch careers to one of these choices:
References:
Image Credit: W.carter via Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
