What is a Machinist?
Machinist Job Description Set up and operate a variety of machine tools to produce precision parts and instruments. Includes precision instrument makers who fabricate, modify, or repair mechanical instruments. May also fabricate and modify parts to make or repair machine tools or maintain industrial machines, applying knowledge of mechanics, mathematics, metal properties, layout, and machining procedures.
Daily Life Of a Machinist
- Set up or operate metalworking, brazing, heat-treating, welding, or cutting equipment.
- Confer with engineering, supervisory, or manufacturing personnel to exchange technical information.
- Dispose of scrap or waste material in accordance with company policies and environmental regulations.
- Evaluate machining procedures and recommend changes or modifications for improved efficiency or adaptability.
- Align and secure holding fixtures, cutting tools, attachments, accessories, or materials onto machines.
- Prepare working sketches for the illustration of product appearance.
Featured schools near , edit
Skills Needed to be a Machinist
Machinists state the following job skills are important in their day-to-day work.
Operation Monitoring: Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
Operation and Control: Controlling operations of equipment or systems.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Coordination: Adjusting actions in relation to others’ actions.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Related Job Titles for this Occupation:
- Experimental Mechanic
- Utility Operator
- Maintenance Machinist
- Set-Up Machinist
- Tool and Die Machinist
Are There Job Opportunities for Machinists?
In the United States, there were 396,200 jobs for Machinist in 2016. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 2% which is below the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 7,900 new jobs for Machinist by 2026. Due to new job openings and attrition, there will be an average of 40,700 job openings in this field each year.
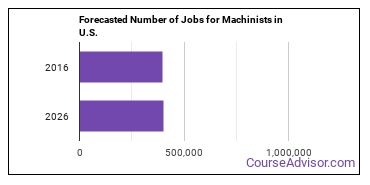
The states with the most job growth for Machinist are Wyoming, Utah, and Arizona. Watch out if you plan on working in Vermont, Maine, or Alaska. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
What is the Average Salary of a Machinist
The typical yearly salary for Machinists is somewhere between $27,050 and $65,360.
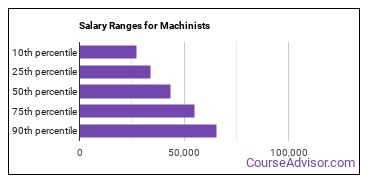
Machinists who work in Alaska, Hawaii, or District of Columbia, make the highest salaries.
How much do Machinists make in different U.S. states?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $44,550 |
| Alaska | $64,220 |
| Arizona | $48,300 |
| Arkansas | $42,180 |
| California | $47,450 |
| Colorado | $48,210 |
| Connecticut | $50,540 |
| Delaware | $55,210 |
| District of Columbia | $62,950 |
| Florida | $42,060 |
| Georgia | $43,900 |
| Hawaii | $66,840 |
| Idaho | $44,610 |
| Illinois | $41,350 |
| Indiana | $44,110 |
| Iowa | $40,080 |
| Kansas | $42,370 |
| Kentucky | $43,810 |
| Louisiana | $49,160 |
| Maine | $51,040 |
| Maryland | $53,560 |
| Massachusetts | $52,700 |
| Michigan | $41,880 |
| Minnesota | $49,880 |
| Mississippi | $41,730 |
| Missouri | $46,130 |
| Montana | $45,590 |
| Nebraska | $43,360 |
| Nevada | $43,850 |
| New Hampshire | $49,060 |
| New Jersey | $50,160 |
| New Mexico | $53,930 |
| New York | $47,010 |
| North Carolina | $42,870 |
| North Dakota | $52,070 |
| Ohio | $42,910 |
| Oklahoma | $44,700 |
| Oregon | $48,930 |
| Pennsylvania | $44,290 |
| Rhode Island | $48,330 |
| South Carolina | $38,610 |
| South Dakota | $38,140 |
| Tennessee | $45,770 |
| Texas | $46,850 |
| Utah | $49,340 |
| Vermont | $44,210 |
| Virginia | $49,640 |
| Washington | $52,190 |
| West Virginia | $37,680 |
| Wisconsin | $43,150 |
| Wyoming | $52,160 |
What Tools do Machinists Use?
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Machinists:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Outlook
- SAP
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- Computer aided design CAD software
- Dassault Systemes CATIA
- Dassault Systemes SOLIDWORKS
- PTC Creo Parametric
- Computer aided manufacturing CAM software
- CNC Mastercam
- ERP software
- Vero Software SURFCAM
- EditCNC
- Kentech Kipware Trig Kalculator
- Mazak Mazatrol SMART CNC
- Autodesk HSMWorks
- CNC Consulting Machinists’ Calculator
Becoming a Machinist
What education or degrees do I need to become a Machinist?
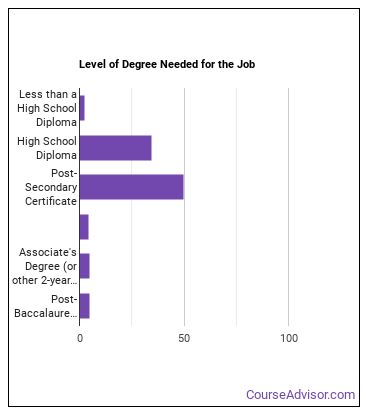
How Long Does it Take to Become a Machinist?
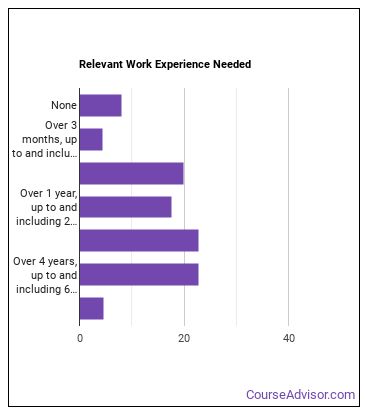
Where Machinists Work
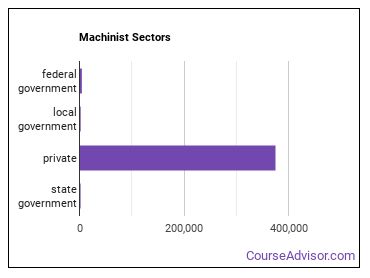
The table below shows some of the most common industries where those employed in this career field work.
You May Also Be Interested In…
Those thinking about becoming a Machinist might also be interested in the following careers:
References:
Image Credit: US Air Force photo/Airman 1st Class John Linzmeier via Public domain
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
