Life As a Geoscientist
Position Description Study the composition, structure, and other physical aspects of the Earth. May use geological, physics, and mathematics knowledge in exploration for oil, gas, minerals, or underground water; or in waste disposal, land reclamation, or other environmental problems. May study the Earth’s internal composition, atmospheres, oceans, and its magnetic, electrical, and gravitational forces. Includes mineralogists, crystallographers, paleontologists, stratigraphers, geodesists, and seismologists.
Life As a Geoscientist
- Locate and review research articles or environmental, historical, or technical reports.
- Develop ways to capture or use gases burned off as waste during oil production processes.
- Identify possible sites for carbon sequestration projects.
- Design geological mine maps, monitor mine structural integrity, or advise and monitor mining crews.
- Identify deposits of construction materials suitable for use as concrete aggregates, road fill, or other applications.
- Research ways to reduce the ecological footprint of increasingly prevalent megacities.
Featured schools near , edit
What Skills Do You Need to Work as a Geoscientist?
These are the skills Geoscientists say are the most useful in their careers:
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Science: Using scientific rules and methods to solve problems.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Related Job Titles
- Project Geophysicist
- Sedimentationist
- Paleontologist
- Geodesist
- Oceanologist
Are There Job Opportunities for Geoscientists?
In the United States, there were 32,000 jobs for Geoscientist in 2016. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 14.1% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 4,500 new jobs for Geoscientist by 2026. The BLS estimates 3,500 yearly job openings in this field.
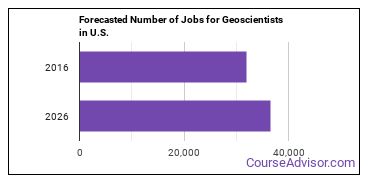
The states with the most job growth for Geoscientist are Tennessee, Colorado, and Oregon. Watch out if you plan on working in West Virginia, Vermont, or North Dakota. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
What is the Average Salary of a Geoscientist
The salary for Geoscientists ranges between about $49,430 and $187,990 a year.
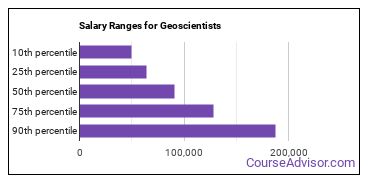
Geoscientists who work in Texas, Oklahoma, or Louisiana, make the highest salaries.
How much do Geoscientists make in each U.S. state?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $64,970 |
| Alaska | $99,400 |
| Arizona | $77,650 |
| Arkansas | $67,260 |
| California | $97,550 |
| Colorado | $111,130 |
| Connecticut | $85,250 |
| Delaware | $80,570 |
| Florida | $80,970 |
| Georgia | $68,860 |
| Hawaii | $109,530 |
| Idaho | $88,060 |
| Illinois | $69,480 |
| Indiana | $61,870 |
| Iowa | $71,490 |
| Kansas | $77,590 |
| Kentucky | $73,230 |
| Louisiana | $109,700 |
| Maine | $74,380 |
| Maryland | $90,110 |
| Massachusetts | $87,650 |
| Minnesota | $78,410 |
| Mississippi | $91,490 |
| Missouri | $70,340 |
| Montana | $92,680 |
| Nebraska | $79,570 |
| Nevada | $94,500 |
| New Hampshire | $95,510 |
| New Jersey | $98,050 |
| New Mexico | $86,620 |
| New York | $76,360 |
| North Carolina | $71,830 |
| North Dakota | $97,320 |
| Ohio | $75,600 |
| Oklahoma | $123,230 |
| Oregon | $74,920 |
| Pennsylvania | $108,580 |
| Rhode Island | $88,130 |
| South Carolina | $72,040 |
| South Dakota | $63,680 |
| Tennessee | $77,510 |
| Texas | $150,140 |
| Utah | $80,970 |
| Virginia | $96,290 |
| Washington | $93,710 |
| West Virginia | $77,530 |
| Wisconsin | $75,110 |
| Wyoming | $73,220 |
Tools & Technologies Used by Geoscientists
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Geoscientists:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Git
- Microsoft Outlook
- Python
- Microsoft Access
- MySQL
- Email software
- Word processing software
- Microsoft Project
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- Adobe Systems Adobe Acrobat
- Adobe Systems Adobe Photoshop
- The MathWorks MATLAB
- SAS
- Geographic information system GIS software
- ESRI ArcView
- Microsoft Active Server Pages ASP
How do I Become a Geoscientist?
Are there Geoscientists education requirements?
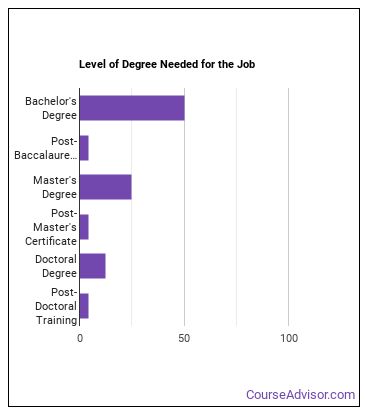
How Long Does it Take to Become a Geoscientist?
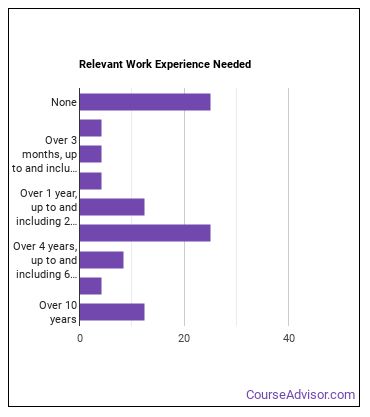
Where do Geoscientists Work?
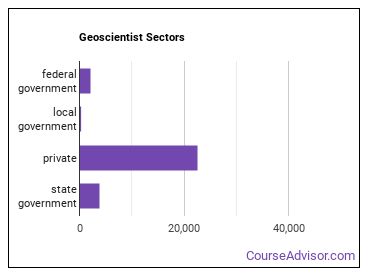
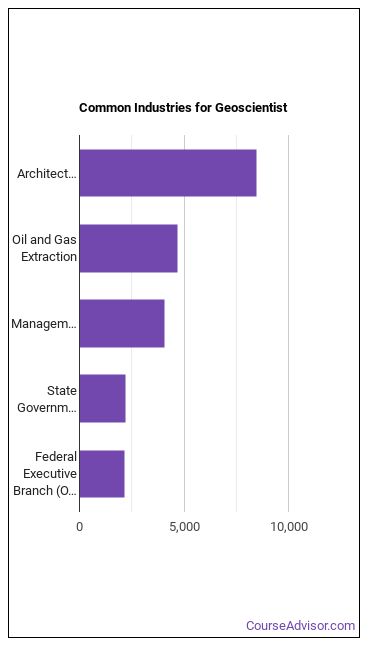
Below are examples of industries where Geoscientists work:
Similar Careers
Those thinking about becoming a Geoscientist might also be interested in the following careers:
Career changers with experience as a Geoscientist sometimes find work in one of the following fields:
References:
Image Credit: Kelvinsong via Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
