What Do Forest and Conservation Technician Do?
Occupation Description Provide technical assistance regarding the conservation of soil, water, forests, or related natural resources. May compile data pertaining to size, content, condition, and other characteristics of forest tracts, under the direction of foresters; or train and lead forest workers in forest propagation, fire prevention and suppression. May assist conservation scientists in managing, improving, and protecting rangelands and wildlife habitats.
Life As a Conservation Technician
- Perform reforestation or forest renewal, including nursery and silviculture operations, site preparation, seeding and tree planting programs, cone collection, and tree improvement.
- Patrol park or forest areas to protect resources and prevent damage.
- Keep records of the amount and condition of logs taken to mills.
- Provide technical support to forestry research programs in areas such as tree improvement, seed orchard operations, insect and disease surveys, or experimental forestry and forest engineering research.
- Inspect trees and collect samples of plants, seeds, foliage, bark, and roots to locate insect and disease damage.
- Provide forestry education and general information, advice, and recommendations to woodlot owners, community organizations, and the general public.
Featured schools near , edit
What Every Conservation Technician Should Know
Forest and Conservation Technicians state the following job skills are important in their day-to-day work.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Judgment and Decision Making: Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Time Management: Managing one’s own time and the time of others.
Related Job Titles for this Occupation:
- Forestry Aide
- Grazing Aide
- Grazing Examiner
- Forest Technician
- Biological Science Aide
Job Outlook for Forest and Conservation Technicians
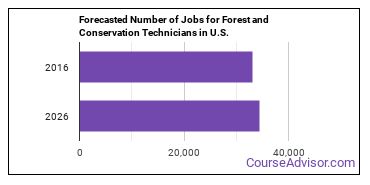
In the United States, there were 33,200 jobs for Forest and Conservation Technician in 2016. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 3.9% which is below the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 1,300 new jobs for Forest and Conservation Technician by 2026. Due to new job openings and attrition, there will be an average of 4,000 job openings in this field each year.
The states with the most job growth for Conservation Technician are Nevada, Florida, and Louisiana. Watch out if you plan on working in Maryland, West Virginia, or Oklahoma. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Do Forest and Conservation Technicians Make A Lot Of Money?
Forest and Conservation Technicians make between $26,600 and $57,700 a year.
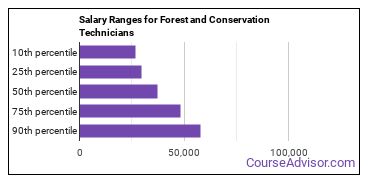
Forest and Conservation Technicians who work in Kansas, Pennsylvania, or Mississippi, make the highest salaries.
How much do Forest and Conservation Technicians make in different U.S. states?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $43,970 |
| Alaska | $47,830 |
| Arizona | $38,270 |
| Arkansas | $46,020 |
| California | $41,010 |
| Colorado | $39,120 |
| Connecticut | $47,150 |
| Florida | $46,050 |
| Georgia | $45,880 |
| Idaho | $37,950 |
| Illinois | $46,650 |
| Indiana | $37,980 |
| Iowa | $39,560 |
| Kansas | $46,180 |
| Kentucky | $37,620 |
| Louisiana | $43,890 |
| Maine | $47,270 |
| Maryland | $43,500 |
| Massachusetts | $47,530 |
| Michigan | $38,350 |
| Minnesota | $44,430 |
| Mississippi | $47,400 |
| Missouri | $43,780 |
| Montana | $37,100 |
| Nebraska | $44,990 |
| Nevada | $38,960 |
| New Hampshire | $39,130 |
| New Mexico | $37,480 |
| New York | $42,070 |
| North Carolina | $40,700 |
| North Dakota | $44,480 |
| Ohio | $40,190 |
| Oklahoma | $45,670 |
| Oregon | $40,490 |
| Pennsylvania | $49,170 |
| South Carolina | $45,500 |
| South Dakota | $37,530 |
| Tennessee | $38,120 |
| Texas | $43,880 |
| Utah | $33,750 |
| Vermont | $41,250 |
| Virginia | $42,080 |
| Washington | $39,900 |
| West Virginia | $41,100 |
| Wisconsin | $35,320 |
| Wyoming | $36,430 |
What Tools & Technology do Forest and Conservation Technicians Use?
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Forest and Conservation Technicians:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Outlook
- Web browser software
- Microsoft Access
- Word processing software
- Spreadsheet software
- Database software
- Computer aided design CAD software
- ESRI ArcView
- Microsoft Active Server Pages ASP
- Desktop publishing software
- Geomechanical design analysis GDA software
- Leica Geosystems ERDAS IMAGINE
- ESRI ArcGIS software
- RockWare ArcMap
- Photogrammetric software
Becoming a Conservation Technician
Individuals working as a Forest and Conservation Technician have obtained the following education levels:
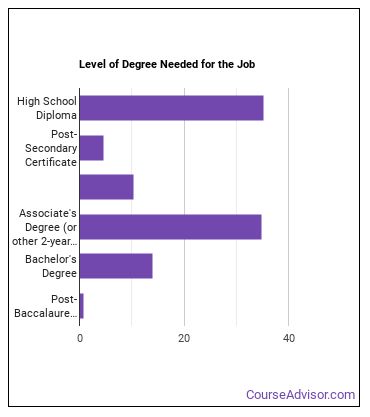
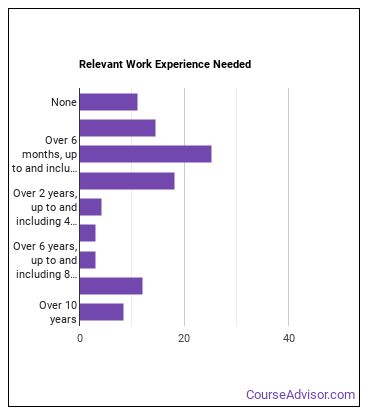
How many years of work experience do I need?
Forest and Conservation Technicians Sector
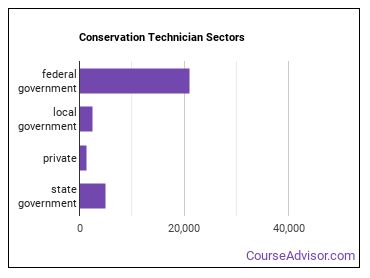
Below are examples of industries where Forest and Conservation Technicians work:
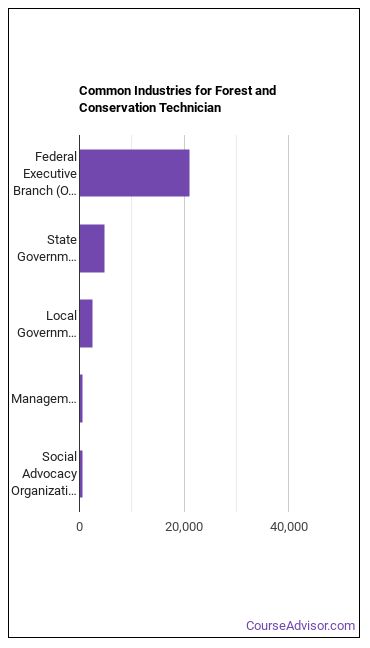
Related Careers
Those thinking about becoming a Forest and Conservation Technician might also be interested in the following careers:
- First-Line Supervisors of Landscaping, Lawn Service, and Groundskeeping Workers
- Forest Firefighters
- Fish and Game Wardens
Those who work as a Forest and Conservation Technician sometimes switch careers to one of these choices:
- Park Naturalists
- Forest Firefighters
- Pesticide Handlers, Sprayers, and Applicators, Vegetation
- Ship and Boat Captains
References:
Image Credit: Bureau of Land Management via Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0)
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
