What is a Biomedical Engineer?
Job Description: Apply knowledge of engineering, biology, and biomechanical principles to the design, development, and evaluation of biological and health systems and products, such as artificial organs, prostheses, instrumentation, medical information systems, and health management and care delivery systems.
A Day in the Life of a Biomedical Engineer
- Develop new applications for energy sources, such as using nuclear power for biomedical implants.
- Advise hospital administrators on the planning, acquisition, and use of medical equipment.
- Keep documentation of service histories on all biomedical equipment.
- Design and deliver technology to assist people with disabilities.
- Conduct training or in-services to educate clinicians and other personnel on proper use of equipment.
- Conduct research, along with life scientists, chemists, and medical scientists, on the engineering aspects of the biological systems of humans and animals.
Featured schools near , edit
Qualities of a Biomedical Engineer
These are the skills Biomedical Engineers say are the most useful in their careers:
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Judgment and Decision Making: Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Science: Using scientific rules and methods to solve problems.
Related Job Titles
- Biomedical Engineering Director
- Biomedical Electronics Technician
- Biomedical Analytical Scientist
- Field Clinical Engineer
- Biomedical Technician
Are There Job Opportunities for Biomedical Engineers?
In 2016, there was an estimated number of 21,300 jobs in the United States for Biomedical Engineer. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 7% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 1,500 new jobs for Biomedical Engineer by 2026. There will be an estimated 1,600 positions for Biomedical Engineer per year.
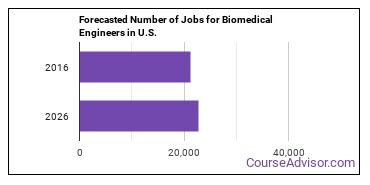
The states with the most job growth for Biomedical Engineer are Utah, Arkansas, and Nebraska. Watch out if you plan on working in Oklahoma, Louisiana, or Illinois. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Biomedical Engineer Salary
The salary for Biomedical Engineers ranges between about $51,890 and $144,350 a year.
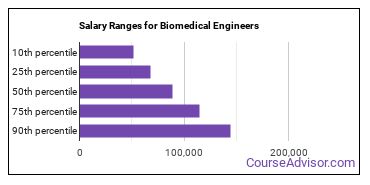
Biomedical Engineers who work in Minnesota, Connecticut, or Maryland, make the highest salaries.
How much do Biomedical Engineers make in different U.S. states?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Arizona | $103,650 |
| Arkansas | $66,840 |
| California | $101,210 |
| Colorado | $96,880 |
| Connecticut | $102,970 |
| District of Columbia | $80,320 |
| Florida | $78,670 |
| Georgia | $81,870 |
| Illinois | $98,420 |
| Indiana | $85,310 |
| Iowa | $68,260 |
| Kansas | $77,150 |
| Maryland | $100,200 |
| Massachusetts | $105,580 |
| Michigan | $79,650 |
| Minnesota | $114,380 |
| Missouri | $75,150 |
| Nebraska | $82,540 |
| Nevada | $96,100 |
| New Jersey | $113,140 |
| New York | $101,460 |
| North Carolina | $93,450 |
| Ohio | $84,700 |
| Oklahoma | $67,300 |
| Oregon | $94,440 |
| Pennsylvania | $78,840 |
| South Carolina | $64,460 |
| Tennessee | $77,920 |
| Texas | $100,680 |
| Utah | $70,980 |
| Vermont | $95,280 |
| Virginia | $97,400 |
| Washington | $94,850 |
| West Virginia | $85,280 |
| Wisconsin | $71,750 |
What Tools do Biomedical Engineers Use?
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Biomedical Engineers may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Hypertext markup language HTML
- JavaScript
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Python
- Microsoft Access
- Word processing software
- Microsoft Windows
- Microsoft Project
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- Microsoft Visio
- Structured query language SQL
- The MathWorks MATLAB
- Microsoft Visual Basic
- Extensible markup language XML
- R
- Computer aided design CAD software
- Minitab
How do I Become a Biomedical Engineer?
What education or degrees do I need to become a Biomedical Engineer?
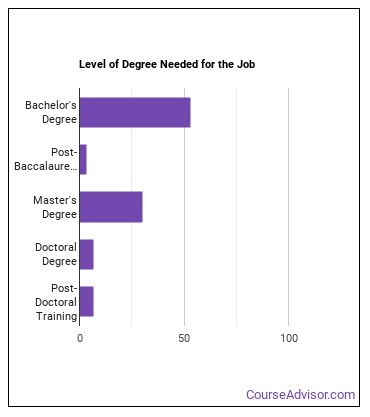
What work experience do I need to become a Biomedical Engineer?
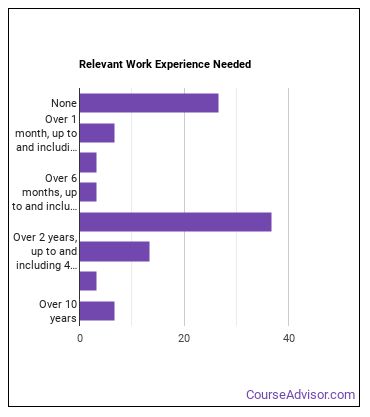
Who Employs Biomedical Engineers?
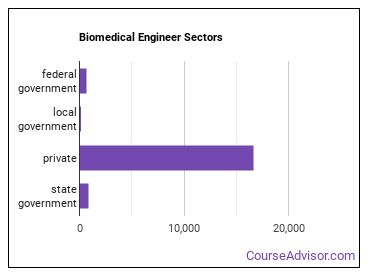
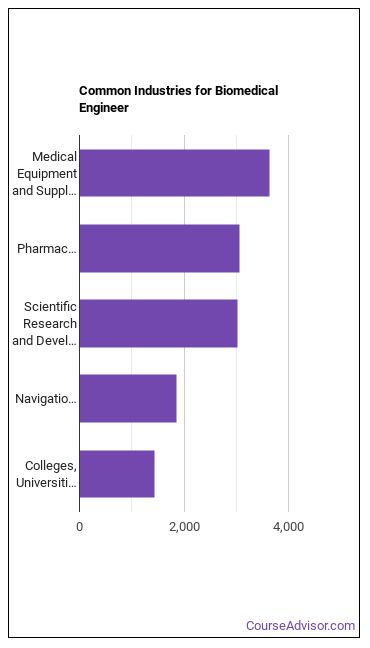
Biomedical Engineers work in the following industries:
Similar Careers
Those interested in being a Biomedical Engineer may also be interested in:
References:
Image Credit: UC Davis College of Engineering via Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
