What is a Precision Agriculture Technician?
Occupation Description Apply geospatial technologies, including geographic information systems (GIS) and Global Positioning System (GPS), to agricultural production or management activities, such as pest scouting, site-specific pesticide application, yield mapping, or variable-rate irrigation. May use computers to develop or analyze maps or remote sensing images to compare physical topography with data on soils, fertilizer, pests, or weather.
Life As a Precision Agriculture Technician: What Do They Do?
- Analyze data from harvester monitors to develop yield maps.
- Draw or read maps, such as soil, contour, or plat maps.
- Demonstrate the applications of geospatial technology, such as Global Positioning System (GPS), geographic information systems (GIS), automatic tractor guidance systems, variable rate chemical input applicators, surveying equipment, or computer mapping software.
- Contact equipment manufacturers for technical assistance, as needed.
- Install, calibrate, or maintain sensors, mechanical controls, GPS-based vehicle guidance systems, or computer settings.
- Analyze remote sensing imagery to identify relationships between soil quality, crop canopy densities, light reflectance, and weather history.
Featured schools near , edit
What a Precision Agriculture Technician Should Know
Below is a list of the skills most Precision Agriculture Technicians say are important on the job.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Active Learning: Understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Judgment and Decision Making: Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Types of Precision Agriculture Technician
- Physical Scientist
- Crop Specialist
- Agronomy Specialist
- GPS Field Data Collector (Global Positioning System Field Data Collector)
- Precision Agriculture Specialist
Precision Agriculture Technician Job Outlook
There were about 76,100 jobs for Precision Agriculture Technician in 2016 (in the United States). New jobs are being produced at a rate of 9.7% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 7,400 new jobs for Precision Agriculture Technician by 2026. Due to new job openings and attrition, there will be an average of 9,900 job openings in this field each year.
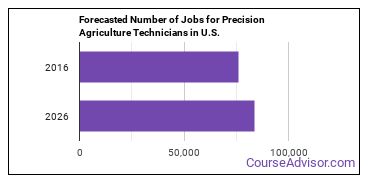
The states with the most job growth for Precision Agriculture Technician are Utah, Texas, and Nevada. Watch out if you plan on working in Wyoming, Maine, or Alaska. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Average Precision Agriculture Technicians Salary
The salary for Precision Agriculture Technicians ranges between about $29,830 and $80,370 a year.
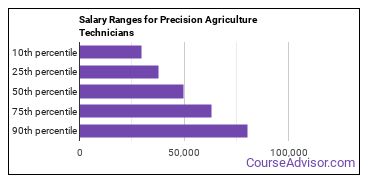
Precision Agriculture Technicians who work in Maryland, Connecticut, or Rhode Island, make the highest salaries.
Below is a list of the median annual salaries for Precision Agriculture Technicians in different U.S. states.
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $46,600 |
| Alaska | $56,470 |
| Arizona | $51,250 |
| Arkansas | $50,740 |
| California | $56,670 |
| Colorado | $51,890 |
| Connecticut | $62,090 |
| District of Columbia | $61,000 |
| Florida | $45,200 |
| Georgia | $52,690 |
| Hawaii | $57,310 |
| Idaho | $42,220 |
| Illinois | $51,130 |
| Indiana | $51,970 |
| Iowa | $46,740 |
| Kansas | $51,960 |
| Kentucky | $52,340 |
| Louisiana | $47,250 |
| Maine | $55,220 |
| Maryland | $69,500 |
| Massachusetts | $63,450 |
| Michigan | $43,640 |
| Minnesota | $50,440 |
| Mississippi | $52,950 |
| Missouri | $49,590 |
| Montana | $43,930 |
| Nebraska | $58,150 |
| Nevada | $47,690 |
| New Hampshire | $57,990 |
| New Jersey | $60,660 |
| New Mexico | $59,850 |
| New York | $53,380 |
| North Carolina | $53,390 |
| North Dakota | $52,050 |
| Ohio | $52,690 |
| Oklahoma | $57,950 |
| Oregon | $51,800 |
| Pennsylvania | $50,410 |
| Rhode Island | $59,480 |
| South Carolina | $56,910 |
| South Dakota | $45,190 |
| Tennessee | $43,440 |
| Texas | $54,290 |
| Utah | $50,980 |
| Virginia | $52,180 |
| Washington | $55,920 |
| West Virginia | $55,930 |
| Wisconsin | $52,500 |
| Wyoming | $53,940 |
What Tools do Precision Agriculture Technicians Use?
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Precision Agriculture Technicians may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Web browser software
- Microsoft Access
- ESRI ArcView
- ESRI ArcGIS software
- ESRI ArcPad
- MapShots EASi Suite
- SST Development Group SSToolbox
- John Deere Apex Farm Management
- Ag Leader Technology SMS Advanced
- Trimble AgGPS EZ-Map
How to Become a Precision Agriculture Technician
What kind of Precision Agriculture Technician requirements are there?
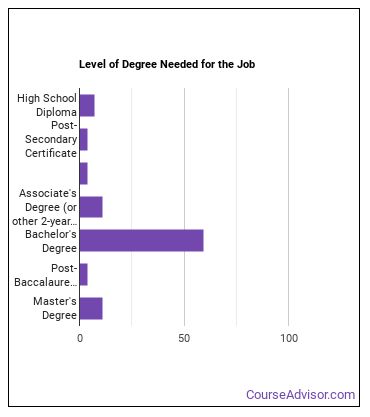
How Long Does it Take to Become a Precision Agriculture Technician?
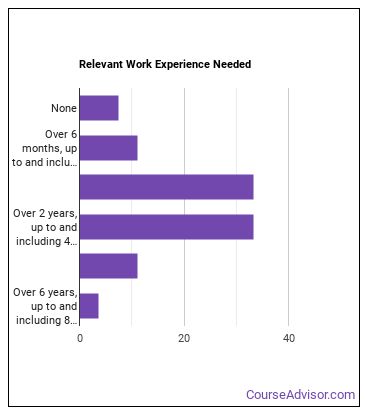
Where Precision Agriculture Technicians Are Employed
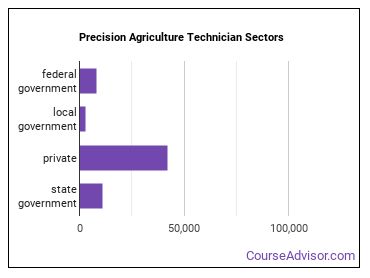
Precision Agriculture Technicians work in the following industries:
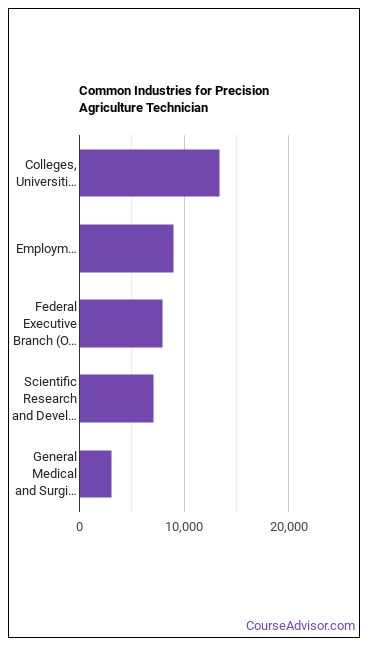
You May Also Be Interested In…
Are you already one of the many Precision Agriculture Technician in the United States? If you’re thinking about changing careers, these fields are worth exploring:
References:
Image Credit: U.S. Department of Energy from United States via public domain
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
