What Do Power Plant Operator Do?
Power Plant Operator Definition Control, operate, or maintain machinery to generate electric power. Includes auxiliary equipment operators.
Daily Life Of a Power Plant Operator
- Clean, lubricate, or maintain equipment, such as generators, turbines, pumps, or compressors, to prevent failure or deterioration.
- Inspect records or log book entries or communicate with plant personnel to assess equipment operating status.
- Operate, control, or monitor equipment, such as acid or gas carbon dioxide removal units, carbon dioxide compressors, or pipelines, to capture, store, or transport carbon dioxide exhaust.
- Control generator output to match the phase, frequency, or voltage of electricity supplied to panels.
- Place standby emergency electrical generators on line in emergencies and monitor the temperature, output, and lubrication of the system.
- Make adjustments or minor repairs, such as tightening leaking gland or pipe joints.
Featured schools near , edit
Skills Needed to be a Power Plant Operator
When polled, Power Plant Operators say the following skills are most frequently used in their jobs:
Operation Monitoring: Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Operation and Control: Controlling operations of equipment or systems.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Quality Control Analysis: Conducting tests and inspections of products, services, or processes to evaluate quality or performance.
Types of Power Plant Operator
- Senior Power Plant Operator
- Carbon Sequestration Plant Engineer
- Plant Operator
- Hydroelectric Operator
- Booster Plant Operator
Power Plant Operator Employment Estimates
In 2016, there was an estimated number of 36,100 jobs in the United States for Power Plant Operator. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 1.1% which is below the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 400 new jobs for Power Plant Operator by 2026. The BLS estimates 3,200 yearly job openings in this field.
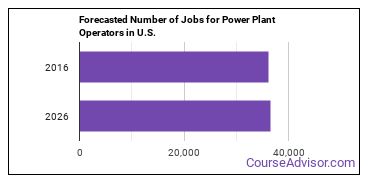
The states with the most job growth for Power Plant Operator are Nevada, Texas, and North Dakota. Watch out if you plan on working in Wisconsin, Montana, or Maine. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
What is the Average Salary of a Power Plant Operator
The typical yearly salary for Power Plant Operators is somewhere between $45,590 and $106,650.
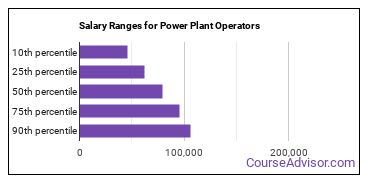
Power Plant Operators who work in California, Washington, or Hawaii, make the highest salaries.
Below is a list of the median annual salaries for Power Plant Operators in different U.S. states.
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $70,890 |
| Alaska | $63,310 |
| Arkansas | $69,980 |
| California | $93,610 |
| Colorado | $78,060 |
| Connecticut | $77,550 |
| Florida | $72,950 |
| Georgia | $70,640 |
| Hawaii | $90,650 |
| Idaho | $68,280 |
| Illinois | $72,060 |
| Indiana | $68,330 |
| Iowa | $77,140 |
| Kansas | $57,030 |
| Kentucky | $80,870 |
| Louisiana | $71,380 |
| Maine | $69,300 |
| Maryland | $87,040 |
| Massachusetts | $79,370 |
| Michigan | $80,420 |
| Minnesota | $82,100 |
| Mississippi | $76,740 |
| Missouri | $76,320 |
| Montana | $83,580 |
| Nebraska | $70,350 |
| Nevada | $87,230 |
| New Hampshire | $67,060 |
| New Jersey | $84,190 |
| New Mexico | $81,690 |
| New York | $87,360 |
| North Carolina | $79,900 |
| North Dakota | $87,130 |
| Ohio | $73,650 |
| Oklahoma | $67,570 |
| Oregon | $79,300 |
| Pennsylvania | $72,550 |
| South Carolina | $71,630 |
| Tennessee | $77,880 |
| Texas | $74,380 |
| Utah | $75,590 |
| Vermont | $63,550 |
| Virginia | $62,360 |
| Washington | $93,600 |
| West Virginia | $65,810 |
| Wisconsin | $67,150 |
| Wyoming | $78,890 |
What Tools & Technology do Power Plant Operators Use?
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Power Plant Operators may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Outlook
- Microsoft Access
- Email software
- Supervisory control and data acquisition SCADA software
- Computerized maintenance management system CMMS
- Distributed control system DCS
- Interlock shutdown systems
How do I Become a Power Plant Operator?
What education or degrees do I need to become a Power Plant Operator?
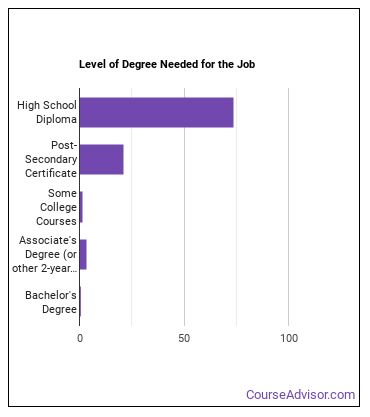
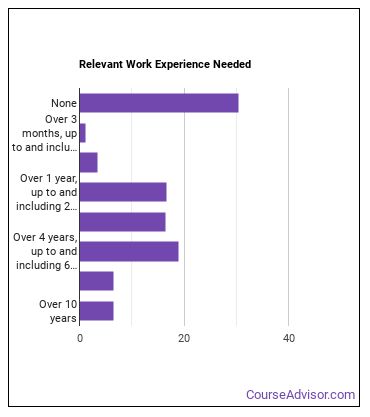
How Long Does it Take to Become a Power Plant Operator?
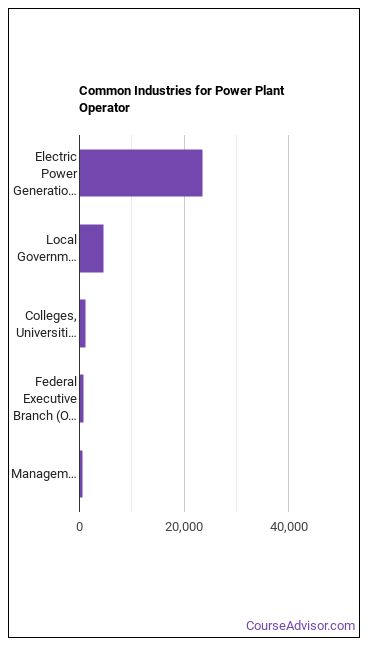
Where do Power Plant Operators Work?
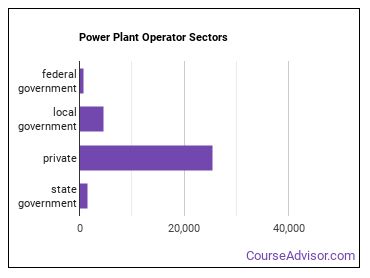
The table below shows the approximate number of Power Plant Operators employed by various industries.
You May Also Be Interested In…
Those thinking about becoming a Power Plant Operator might also be interested in the following careers:
Those who work as a Power Plant Operator sometimes switch careers to one of these choices:
References:
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
