What Does it Take to Be a Machine Tool Operator?
Machine Tool Operator Job Description Operate computer-controlled machines or robots to perform one or more machine functions on metal or plastic work pieces.
Life As a Machine Tool Operator: What Do They Do?
- Confer with supervisors or programmers to resolve machine malfunctions or production errors or to obtain approval to continue production.
- Monitor machine operation and control panel displays and compare readings to specifications to detect malfunctions.
- Control coolant systems.
- Remove and replace dull cutting tools.
- Implement changes to machine programs and enter new specifications, using computers.
- Modify cutting programs to account for problems encountered during operation and save modified programs.
Featured schools near , edit
Machine Tool Operator Required Skills
When polled, Machine Tool Operators say the following skills are most frequently used in their jobs:
Operation Monitoring: Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
Monitoring: Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Quality Control Analysis: Conducting tests and inspections of products, services, or processes to evaluate quality or performance.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Operation and Control: Controlling operations of equipment or systems.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Types of Machine Tool Operator
- Computer Numerically Controlled Shot Peening Operator
- Computer Numerical Control Mill Operator (CNC Mill Operator)
- Computer Numerical Control Operator (CNC Operator)
- Computer Numerical Control Set-Up and Operator (CNC Set-Up and Operator)
- Medical Numerical Control Operator
Job Opportunities for Machine Tool Operators
In 2016, there was an estimated number of 145,700 jobs in the United States for Machine Tool Operator. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 1.1% which is below the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 1,600 new jobs for Machine Tool Operator by 2026. There will be an estimated 14,500 positions for Machine Tool Operator per year.
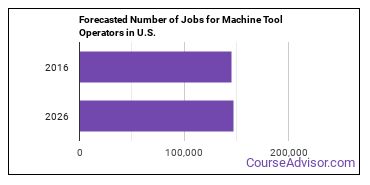
The states with the most job growth for Machine Tool Operator are Utah, North Dakota, and Montana. Watch out if you plan on working in Vermont, New Mexico, or Washington. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Machine Tool Operator Salary
Machine Tool Operators make between $26,890 and $60,650 a year.
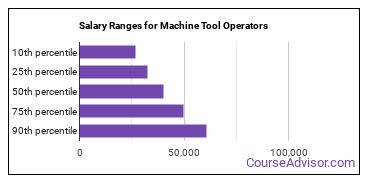
Machine Tool Operators who work in Washington, Massachusetts, or North Dakota, make the highest salaries.
How much do Machine Tool Operators make in different U.S. states?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $38,170 |
| Arizona | $38,820 |
| Arkansas | $37,780 |
| California | $42,930 |
| Colorado | $43,990 |
| Connecticut | $47,240 |
| Delaware | $35,700 |
| Florida | $38,960 |
| Georgia | $37,510 |
| Idaho | $38,730 |
| Illinois | $39,570 |
| Indiana | $39,700 |
| Iowa | $40,740 |
| Kansas | $42,650 |
| Kentucky | $36,110 |
| Louisiana | $45,920 |
| Maine | $47,530 |
| Maryland | $44,080 |
| Massachusetts | $51,150 |
| Michigan | $40,500 |
| Minnesota | $45,670 |
| Mississippi | $36,250 |
| Missouri | $39,730 |
| Montana | $40,430 |
| Nebraska | $38,970 |
| Nevada | $42,850 |
| New Hampshire | $45,220 |
| New Jersey | $45,750 |
| New Mexico | $36,360 |
| New York | $38,700 |
| North Carolina | $38,780 |
| North Dakota | $49,590 |
| Ohio | $41,760 |
| Oklahoma | $39,730 |
| Oregon | $43,560 |
| Pennsylvania | $39,870 |
| Rhode Island | $42,710 |
| South Carolina | $43,220 |
| South Dakota | $38,630 |
| Tennessee | $39,140 |
| Texas | $41,560 |
| Utah | $35,220 |
| Virginia | $41,110 |
| Washington | $64,290 |
| West Virginia | $43,590 |
| Wisconsin | $44,190 |
Tools & Technologies Used by Machine Tool Operators
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Machine Tool Operators may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- SAP
- Microsoft Project
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- Computer aided design CAD software
- Dassault Systemes CATIA
- Dassault Systemes SOLIDWORKS
- PTC Creo Parametric
- Computer aided manufacturing CAM software
- 1CadCam Unigraphics
- CNC Mastercam
- ERP software
- Delcam PowerMILL
- MUMPS M
- UGS Solid Edge
- G-code
- Vero Software SURFCAM
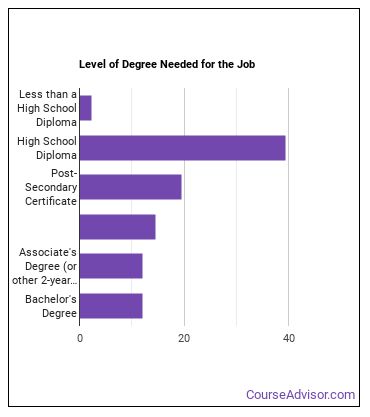
How do I Become a Machine Tool Operator?
Learn what Machine Tool Operator education requirements there are.
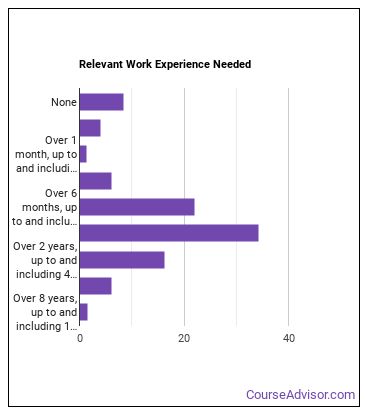
How many years of work experience do I need?
Where do Machine Tool Operators Work?
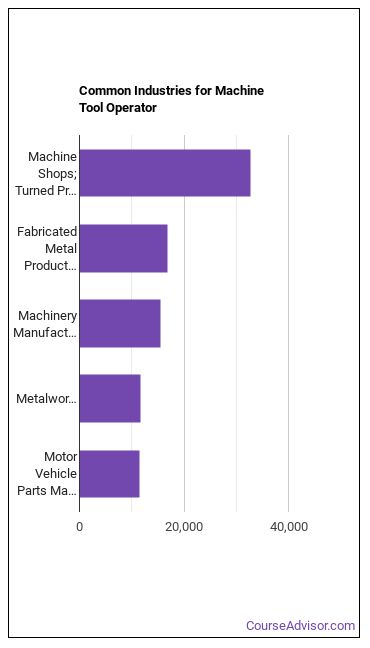
Machine Tool Operators work in the following industries:
Similar Careers
Those who work as a Machine Tool Operator sometimes switch careers to one of these choices:
References:
Image Credit: US Air Force photo/Airman 1st Class John Linzmeier via Public domain
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
 Request Info
Request Info
|
Southern New Hampshire University You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs. Learn More > |
